ArcGIS Notebook Server supports multiple-machine sites starting at 10.7.1. In a multiple-machine site, each machine is configured the same, with identical Docker setups, and each can run ArcGIS Notebooks.
Multiple-machine ArcGIS Notebook Server sites allow you to support more simultaneous notebook users. If you have many active users, or if your single machine's resources are inadequate for your users' needs, expanding to a multiple-machine site could be beneficial.
Note:
If you have a few notebook users who require more machine resources, you might evaluate modifying your site's resource limits as a limited alternative to adding machines.
All machines in an ArcGIS Notebook Server site have the same software installed, with the same version and the same license file. On the first machine you set up, you'll need to create the ArcGIS Notebook Server site. You can then join additional ArcGIS Notebook Server machines to the site.
Note:
Unlike other ArcGIS Server roles, ArcGIS Notebook Server does not support adding additional machines to a site from the first machine. You must access each machine in turn and join them to the site, using the ArcGIS Notebook Server configuration wizard or the joinsite utility.
Before you install
When you create a site, you determine where to store the configuration store, a directory hosting the critical files and configuration information for your site. Your site also has system and workspace server directories.
When you first create an ArcGIS Notebook Server site, you specify locations for the configuration store and server directories. In a multiple-machine site, you must share the configuration store and server directories so that the other machines can access them. Each machine that joins the site must be granted read and write permissions to these shared locations.
Shared drives and replication
In multiple-machine ArcGIS Notebook Server sites, most server directories and the site configuration store are hosted on shared locations accessible to each machine. The exception is the workspace directory, which is mounted to each user's Docker containers. Docker does not support mounting shared drives to containers in Windows systems, so the workspace directory must remain local on each machine. Because users can launch containers and open notebooks on any machine in a multiple-machine site, it's necessary that the content in the workspace directory be synchronized across machines.
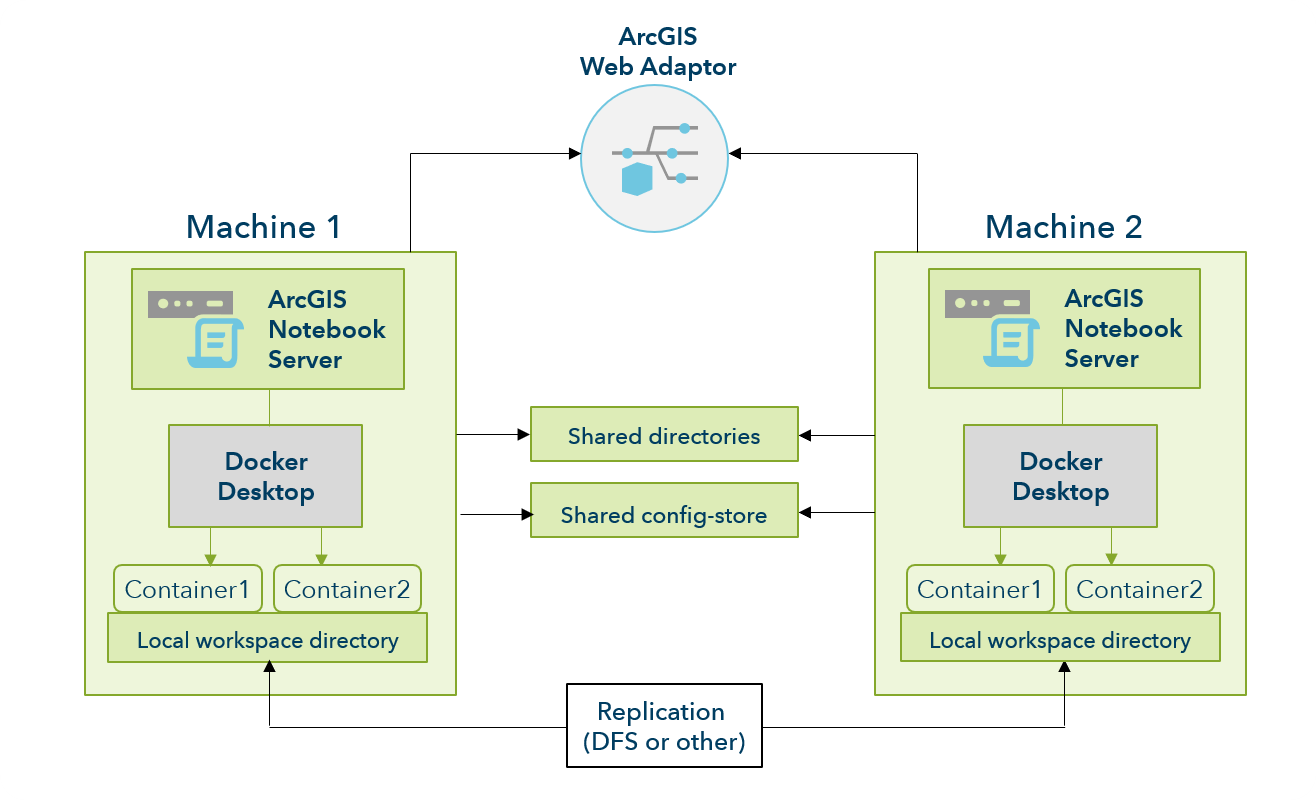
Windows offers a native replication solution: Distributed File System (DFS) data replication, which synchronizes data across machines efficiently by only synchronizing any data packets that have changed, rather than entire items. When using DFS, the folder to be replicated is kept in an identical location on each machine.
DFS replication is not the only possible way to synchronize the contents of your ArcGIS Notebook Server site's workspace directory. But because it is a frequently used method native to Windows, the steps to set it up are given in Configure DFS replication for ArcGIS Notebook Server. You can discuss with your IT administrator whether DFS or another replication system is best for your organization.
Install and configure a multiple-machine site
When you intend to set up a multiple-machine ArcGIS Notebook Server site, there are some additional steps to follow in this installation guide.
- Review the system requirements for ArcGIS Notebook Server to verify that each machine qualifies. On each machine, adjust the firewalls to open port 11443 for communication from each machine in your ArcGIS Enterprise deployment.
The installed version of ArcGIS Notebook Server and its license file must be the same on each machine. Enter the same ArcGIS Notebook Server account during each installation. It's recommended that you use a domain or Active Directory account, but if you choose a local account, it needs to exist on each machine with an identical name and password combination. Keep in mind that the account you specify does not have to be part of the Administrators group.
- Ensure that you have already done the following during the installation process to this point:
- Install Docker on each machine. On each machine, download the Docker images provided by Esri and save them to a location the system can access.
- Install and authorize ArcGIS Notebook Server on each machine. You can also silently install the software.
- Run the command line PostInstaller utility (located at <ArcGIS Notebook Server installation directory>\tools\postInstallUtility) to load the Docker images into the local repository on each machine.
- Follow the steps to configure ArcGIS Notebook Server after installation.
- Create and share two directories on your network. One should be for the configuration store and the other for some of the server directories. The workspace directory should remain on a local path. Grant read and write permissions for these two directories to the ArcGIS Notebook Server account on each machine (make sure to do this on both the Sharing tab and the Security tab of Windows Explorer).
Note:
Shared network directories that are hidden or use special characters (such as $) are not supported by ArcGIS Notebook Server.
- Even if the directories reside on the same machine that you will use when creating the site, you must still manually create and share the directories and reference them through a network (UNC) path.
- If the ArcGIS Notebook Server account does not exist on the machine (in the case where you put the configuration store and server directories on a file server), you need to create the ArcGIS Notebook Server account using the same name and password that you used in all the other machines in your deployment.
- From one of your machines, create a new ArcGIS Notebook Server site. Ensure you use the paths for your server directories and configuration store that you set up earlier.
- Once the previous steps have been completed, you can join each additional machine to the site you've created using a configuration wizard. If you prefer to join the site from the command line, see step 6.
- From the first additional machine, open the ArcGIS Notebook Server Configuration Wizard.
- Review and follow the instructions provided in the wizard, and then click Continue.
- Click Join Existing Site.
- Enter the site URL and credentials for your ArcGIS Notebook Server site as created in step 4.
- Repeat steps a through d for each additional machine you want to join to the site.
- As an alternative to using the configuration wizard, you can join the machine to the site using a command line utility as follows.
- Ensure you're logged in to the machine with the ArcGIS Notebook Server account.
- Open a command prompt and run the utility, which is located at <ArcGIS Notebook Server install directory>\tools\JoinSiteUtility\joinsite.bat. The command line parameters for the utility are:
Parameter Description -u or --username
The username of the primary site administrator.
-p or --password
The password for the primary site administrator.
-s or --siteUrl
The URL of the existing ArcGIS Notebook Server site to join, in the format https://notebookserver.domain.com:11443/arcgis/admin.
-h or --help
Displays command line help and exits.
An example command for the utility:
<ArcGIS Notebook Server install directory>\tools\JoinSiteUtility\joinsite.bat -u notebookPSA -p my.Password3 -s https://notebookserver.domain.com:11443/arcgis/adminIf the account credentials and site URL are entered correctly, the utility will join the machine to the ArcGIS Notebook Server site. Repeat this step for each additional machine.
At this point, you can set up a replication system for the workspace directory across your ArcGIS Notebook Server machines. The steps to set up one option for replication are given in Configure DFS replication for ArcGIS Notebook Server. You can set up a replication system at any point during the installation process.
Once all the machines are joined to the site, the remaining setup process is the same as for single-machine sites. Proceed to install and configure ArcGIS Web Adaptor with your site. You will then configure your site with your ArcGIS Enterprise portal.